Male patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 are more likely to have urinary disorders
Research published in the Journal of Internal Medicine shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection worsens lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men.
introduce
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) affects extrarespiratory system, small study suggests worsening lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) Men after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
This study explores the association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and complications benign prostatic hyperplasia (Male BPH) using large-scale real-world data.
Materials and methods
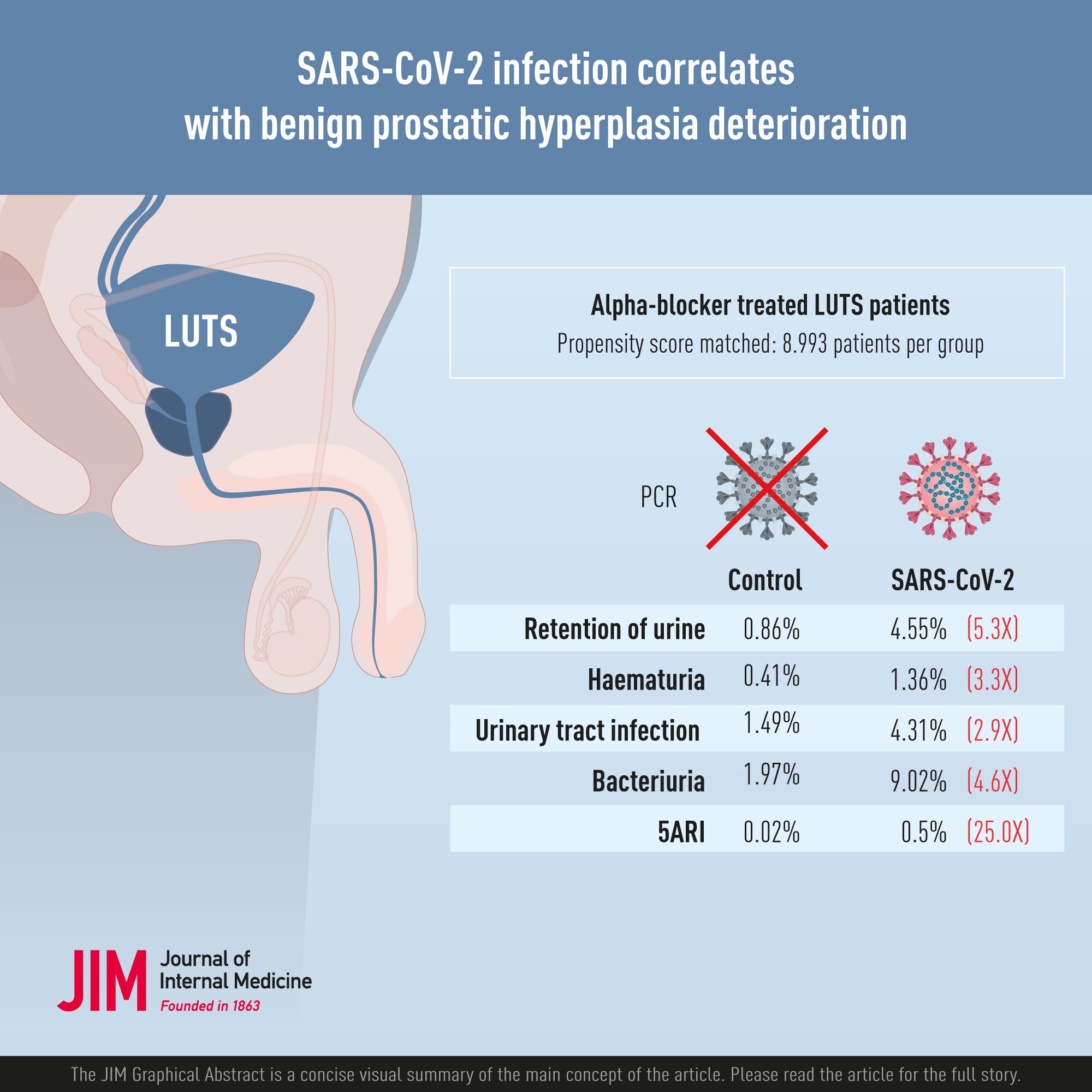
This study included all male patients who visited the Hong Kong public health system from 2021 to 2022 and received α-blocker monotherapy for LUTS.
Patients with positive and non-positive SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests were selected as the exposure group and control group, respectively.
Baseline characteristics were retrieved and propensity score matching was performed to ensure balance of covariates between the two groups. Complications of BPH were then compared and subgroup analysis was performed.
result
After propensity score matching, include it in the analysis 17,986 patientshalf of whom were confirmed to be infected with SARS-CoV-2 by PCR (n = 8993).
Compared with the control group, the SARS-CoV-2 group had significantly higher incidences of urinary retention (4.55% vs 0.86%, p < 0.001), hematuria (1.36% vs 0. .41%, p < 0.001), and clinical urine routine. rising. Urinary tract infection (UTI) symptoms (4.31% vs 1.49%, p < 0.001), culture-proven bacteriuria (9.02% vs 1.97%, p < 0.001) and addition of 5ARI (0.50% vs 0.02%, p < 0.001 ).
Subgroup analysis showed similar differences across age groups. There were no statistically significant differences in the incidence of retention, hematuria, or the addition of 5ARI between different severities of COVID-19.
|
in conclusion
Regardless of COVID-19 severity, SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with higher rates of urinary retention, hematuria, UTIs, and increased short-term combination therapy. This is the largest study to demonstrate the harmful effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the urinary system.
|
Comment

