https://sputniknews.lat/20230813/descubren-que-la-polucion-atmosferica-eleva-la-resistencia-a-los-antibioticos-1142565328.html
Air pollution increases resistance to antibiotics, they find
Air pollution increases resistance to antibiotics, they find
Antibiotic immunity poses a growing threat to global health. In 2019, it killed more than 1.27 million people worldwide and is expected to… 08.13.2023, Sputnik
2023-08-13T18:21+0000
2023-08-13T18:21+0000
2023-08-13T18:21+0000
science
💗 health
environment
pollute
antibiotic
tuberculosis
disease
bacteria
Infect
immunity
/html/head/meta(@name=”og:title”)/@content
/html/head/meta(@name=”og:description”)/@content
https://cdn2.img.sputniknews.lat/img/106155/45/1061554589_0:213:3611:2244_1920x0_80_0_0_e6fdee1f538568fd834348015c4f4c9a.jpg
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, and their misuse and overuse can lead to the growth of bacteria that contain genes that make them resistant to the killing power of these drugs. This, in turn, makes it difficult to treat certain infections. It has long been known that this tolerance is transmitted to humans primarily through contaminated food or water. But a recent study published in The Lancet suggests that’s not the only way air pollution can spread antibiotic resistance, too. A research team of Chinese and British professionals focused on the most dangerous form of air pollution: PM2.5. These particles are 2.5 microns in diameter, about 3% the diameter of a human hair. PM2.5 is invisible to the naked eye and is easily inhaled. They compiled results from 12 trials conducted in 116 countries, including the UK, US, India and Australia. They found that as the concentration of PM2.5 in the air increased, so did the resistance to these drugs. A 10 percent increase in PM2.5 concentrations was associated with a 1.1 percent increase in global antibiotic resistance, resulting in 43,654 deaths from antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, with resistance highest in North Africa and West Asia, the report said. PM2.5 pollution in these areas is also relatively serious. In contrast, European and North American regions with the lowest average levels of PM2.5 pollution also had the lowest immunity, for example, a 1% increase in PM2.5 in all regions was associated with increased tolerance to PM2.5. Klebsiella pneumoniae, a bacterium that often spreads in hospitals and causes pneumonia, meningitis, urinary tract infections and even cancer, requires multiple antibiotics, the article said. Other reports suggest that air pollution is also a risk factor for tuberculosis, which is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which has also successfully developed immunity to many of these drugs. Thus, a study in Hong Kong also revealed an association between outdoor exposure to PM2.5 and tuberculosis. He also found that increases in PM2.5 concentrations in winter were associated with a 3% increase in the number of TB cases in the following seasons (ie, spring and summer). However, the underlying mechanisms that may contribute to the spread of TB, while the link between the two is clear, the impact of antimicrobial resistance in air pollution remains unclear. The cited article only reinforces the argument for urgently improving air quality and reducing global pollution.
https://sputniknews.lat/20230307/there-is-no-place-on-earth-where-you-can-be-safe-from-contamination-present-in-the-air–1136554060.html
2023
information
es_ES
💗 Health, environment, pollution, antibiotics, tuberculosis, disease, bacteria, infection, immunity
💗 Health, environment, pollution, antibiotics, tuberculosis, disease, bacteria, infection, immunity
Antibiotic immunity poses a growing threat to global health. It killed more than 1.27 million people worldwide in 2019, and antimicrobial resistance is expected to kill 10 million people a year by 2050.
The research team, made up of Chinese and British professionals, specializes in the most dangerous types of air pollution: PM2.5. These particles are 2.5 microns in diameter, about 3% the diameter of a human hair. PM2.5 is invisible to the naked eye and is easily inhaled.
They compiled results from 12 trials conducted in 116 countries, including the UK, US, India and Australia.
They found increased resistance to these drugs at the same time Higher than the concentration of PM2.5 in the air. For every 10% increase in PM2.5 concentration, antibiotic resistance increased by 1.1% overall, 43,654 deaths Caused by an infection with drug-resistant bacteria.
According to the report, the level higher resistance They are recorded in North Africa and Western Asia. PM2.5 pollution in these areas is also relatively serious.In contrast, Europe and North America, with the lowest average levels of PM2.5 pollution, also hit new highs Lower immunity.
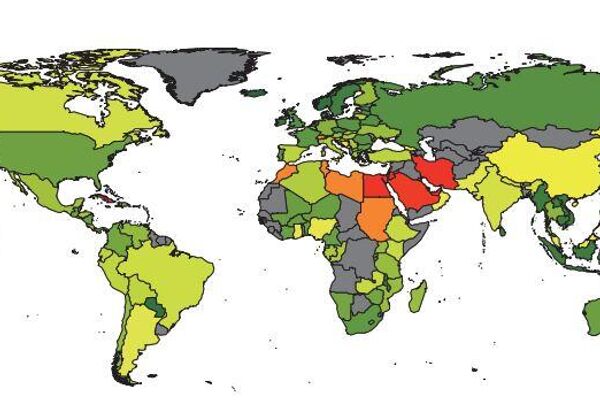
Contribution of PM2.5 to antibiotic resistance in different countries and regions
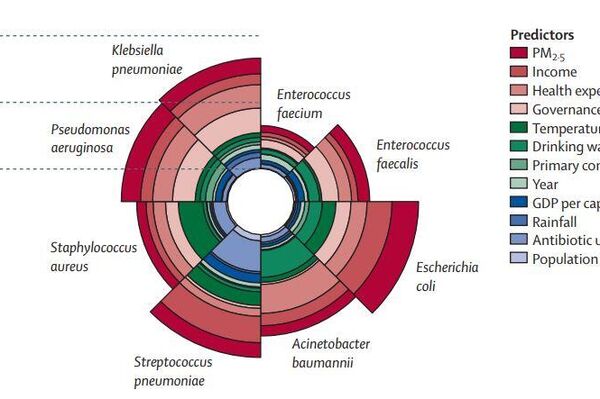
Contribution of predictors to antibiotic resistance for each pathogen
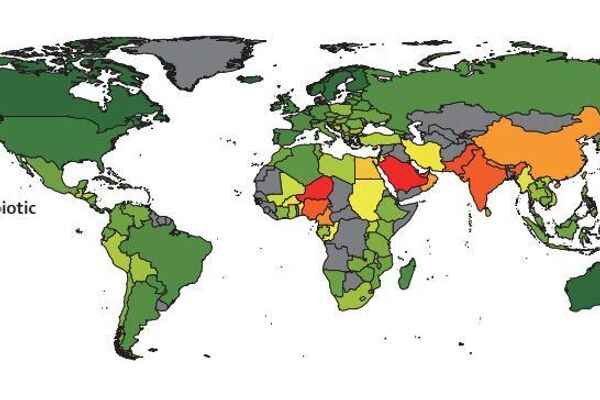
Antibiotic resistance changes for every 10% change in PM2.5 concentrations
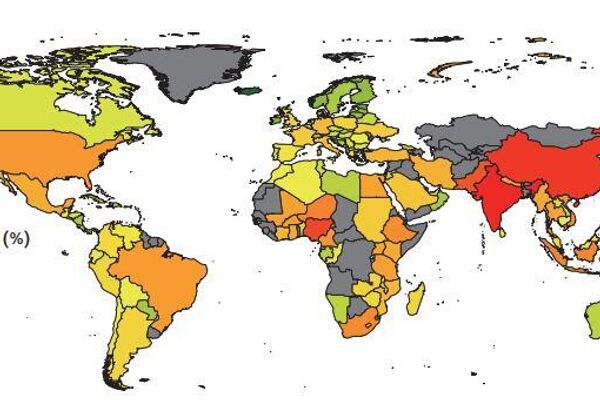
A 10% change in PM2.5 concentrations was associated with a change in premature death from antibiotic resistance.
Contribution of PM2.5 to antibiotic resistance in different countries and regions
Contribution of predictors to antibiotic resistance for each pathogen
Antibiotic resistance changes for every 10% change in PM2.5 concentrations
A 10% change in PM2.5 concentrations was associated with a change in premature death from antibiotic resistance.
Thus, a study in Hong Kong also revealed an association between outdoor exposure to PM2.5 and tuberculosis. He also found that increases in PM2.5 concentrations in winter were associated with a 3% increase in the number of TB cases in the following season (ie, 2019). spring and summer.


Don’t miss the most important news
Subscribe to our Telegram channel via these links.
Since the Sputnik app is blocked abroad, you can download and install it on your mobile device via this link (Android only!).
We also have an account on the Russian social network VK.

